Sweet potatoes are a super food that I have only recently come to appreciate. While preparing a lecture on heart disease epidemiology, I found reports of several traditional cultures known for avoiding heart disease that subsist largely on this delicious tuber. In fact, a 1978 paper[1] cited a dietary survey finding that sweet potatoes supplied about 90% of total calorie intake in the traditional subsistence culture of the Papua New Guinea highlanders. 90%! Sinnett and Whyte write, “Indeed, non-tuberous vegetables accounted for less than 5% of the food consumed, while the intake of meat was negligible.” There was no evidence of malnutrition from this diet and no evidence for hypertensive heart disease.
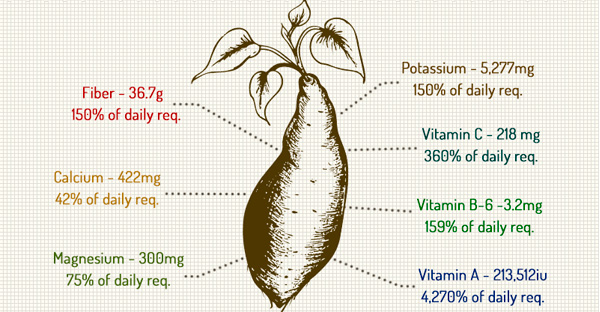
Here are some facts to chew on. If HALF of your diet was solely baked sweet potatoes with no salt, you would get all the nutrients in the table. To top it off: you get all this in a package with a lower glycemic index than white potatoes and many grains[2].
Percentage of daily requirements (2000kcal diet)*
* Nutrient amounts calculated from USDA, reference 3, using the average daily requirements listed on http://www.dsld.nlm.nih.gov/dsld/dailyvalue.jsp
Copyright 2025 Center for Nutrition Studies. All rights reserved.